Introduction To Ciphers
History of Ciphers.
The need to conceal messages has been with us since we moved out of caves, started living in groups and decided to take this civilization idea seriously. As soon as there were different groups or tribes, the idea that we had to work against each other surfaced and was proliferated, along with secrecy and crowd manipulation. The earliest forms of secret communications were found in the early civilization of Egypt, Greece and Rome. They used differnt forms of cipher techniques to keep the messages hidden from others.
What is a Cipher?
It is a way of producing secret messages/text so that the actual meaning or secret message remains hidden unless you know how to decode the ciphered text.
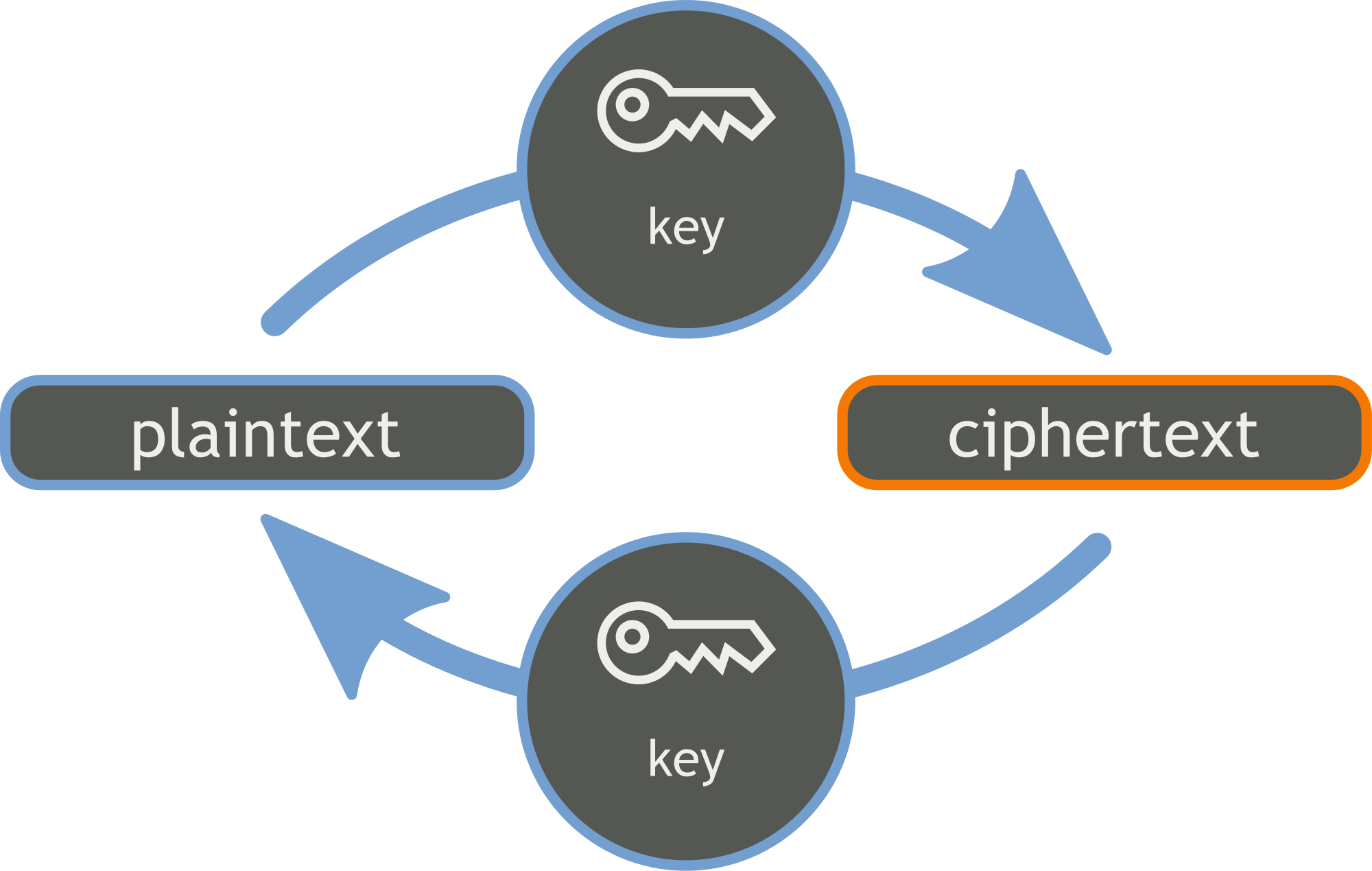
In cryptography, a cipher is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption -a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is encipherment. To encipher or encode is to convert information into cipher or code. In common parlance, “cipher” is synonymous with“code”, as they are both a set of steps that encrypt a message; however, the concepts are distinct in cryptography, especially classical cryptography.
The text before encryption is known as plaintext whereas text after adding encryption is known as ciphered/encrypted text.
Sounds exciting? Find out more!
Easy !
Hard !!
Difficult !!!
 Secret Communications
Secret Communications